0 Comments
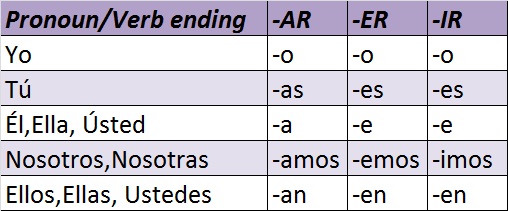
Regular verbs are those verbs that end in -ar;-er;-ir. Their conjugation in the simple present is quite simple. Just look at the chart below. To conjugate a verb in the simple present follow the next directions:
One more example with the verb leer:
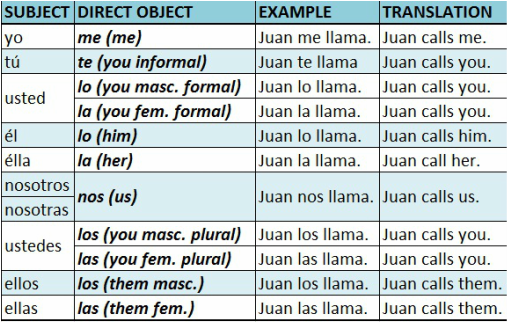
Los pronombres de complemento directo en español-Spanish direct object pronouns-simple present8/12/2015 A Direct Object pronoun is a noun or pronoun that receives the verb's action. For example: Yo pateo la pelota. (I kick the ball) Yo la pateo (I kick it) Yo=subject; pateo=verb; la pelota=direct object. Notice how the direct object pronoun in Spanish is placed between the subject and the main verb.
The following chart shows the correspondent object pronoun for each personal pronoun.
Comparative forms in Spanish follow a simple pattern Let's compare some pets, people, and objects: El gato es más rápido que el perro. (The cat is faster than the dog.) El ratón es más pequeño que el elefante. (The mouse is smaller than the elephant.) Mi padre es más alto que mi madre. (My father is taller than my mother) Mi hermano es menos hablador que mi hermana. (My brother is less talkative than my sister.) La historia es más difícil que la matemática. (History is harder than mathematics.) *Notice that the word "más" has a tilde (á) as it refers to an increase on something. Without it "mas" means but.
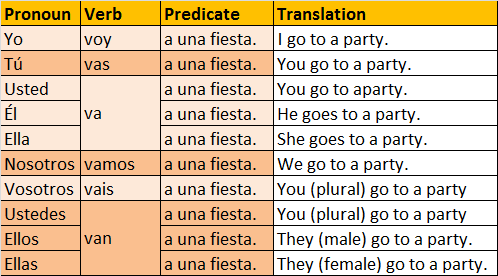
One of the easiest ways to express the future in Spanish is by using the irregular verb "ir" plus one more verb in its infinitive form (termination in -ar,-er,ir) This grammar is quite similar to the "be going to" form in English.
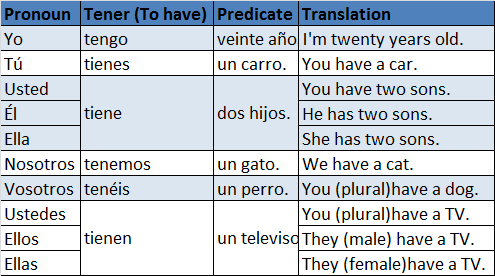
For example: Yo voy a viajar a México mañana. (I'm going to travel to Mexico tomorrow.) To form the negative you use need to add the word "No" before the verb "ir" conjugated. For example: Yo no voy a viajar a Mexico mañana. (I'm not going to travel to Mexico tomorrow.) If you want to make questions in this form you just need to place the questions marks (¿?) at the begining and the end of the sentence. In speaking you need to use some sort of raising intonation. Very similar to the one you use when asking questions like Do you like coffe? in English. For example: Affirmative: (Ellos) van a tomar un táxi. (They are going to take a taxi.) Question: ¿Van a tomar un táxi? (Are they going to take a taxi?) The verb "tener" in Spanish is equivalent to the verb have in the sense of possession. Notice that the first example "Yo tengo veinte años" means I'm twenty years old. In Spanish, age is thought to be possessed and that is why this is the appropriate form to describe ages. Common questions with the verb "tener" are:
The irregular verb "ir" in Spanish is equivalent to the verb "to go in English"; however, its conjugation for each personal pronoun is as follows:
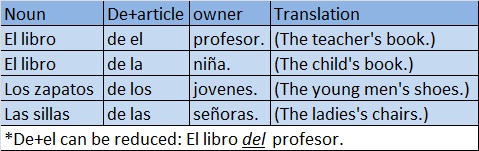
The Spanish possessive forms with "DE" are equivalent to the possessive English form 's. They follow the formula Object-De+article+owner. Only in the case of the singular masculine can "de" and the article "el" be contracted.
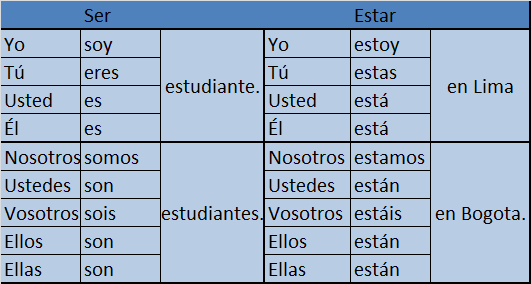
Ser and its conjugations express Profession, Nationality, Origin, Basic characteristics.
SON LAS nueve Y veinticuatro DE LA MAÑANA.Follow these easy steps to tell the time in Spanish:
(Notice that ES is used only with UNA. For the rest of hours you'll use SON Es la una y treinta de la tarde.
|
Spanish tutorsHello there!! Categories
All
|






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed